What Direction Is the Gravitational Force of the Orbiting Object
Mass has yet another role to play. These orbiting bodies can be a planet and its satellite a star and any object orbiting it or components of any binary system.

Question Video Identifying Forces And Velocities Of A Planet Orbiting A Star Nagwa
To the Earths gravitational pull.

. A black hole can be formed by the death of a massive star. A geocentric orbit or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Earth such as the Moon or artificial satellitesIn 1997 NASA estimated there were approximately 2465 artificial satellite payloads orbiting Earth and 6216 pieces of space debris as tracked by the Goddard Space Flight Center. Orbits do not decay without some friction-like mechanism which transfers energy from the orbital motion.
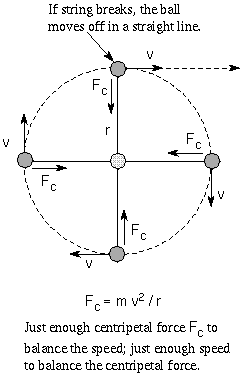
More than 16291 objects previously launched have undergone orbital decay and entered. When such a star has exhausted the internal thermonuclear fuels in its core at the end of its life the core becomes unstable and gravitationally collapses inward upon itself and the stars outer layers are blown. For an object moving in a circle this resultant force is the centripetal force.
This can be any of a number of mechanical gravitational or electromagnetic effects. That acts towards the middle of the circle. But an objects charge also determines the.
Gravitational attraction provides the centripetal force needed to keep. Black hole cosmic body of extremely intense gravity from which nothing not even light can escape. So far weve introduced the gravitational charge as a measure for how strongly an object reacts to the gravitational pull of other bodies eg.
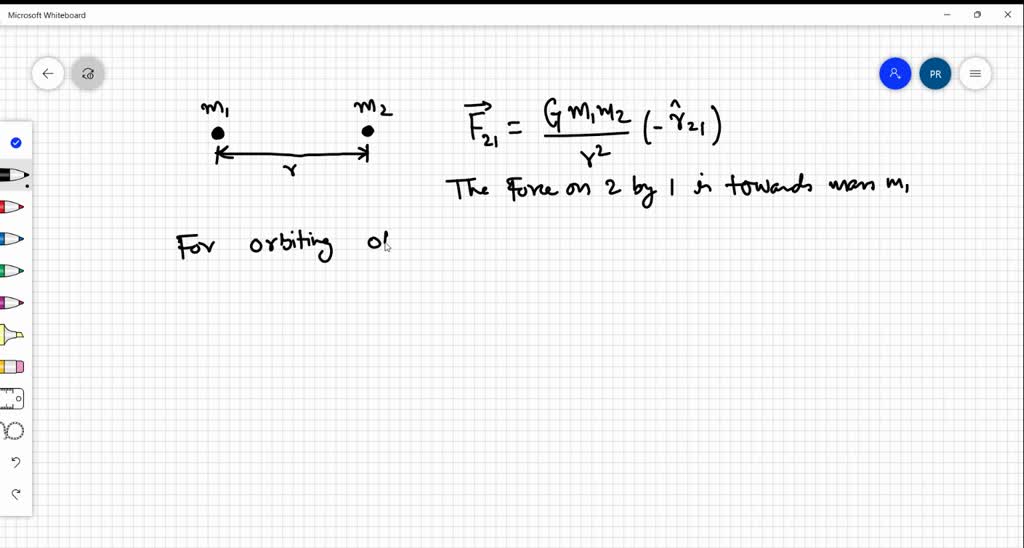
Solved 1 What Direction Is The Gravitational Force Of The Orbiting Objects
Comments
Post a Comment